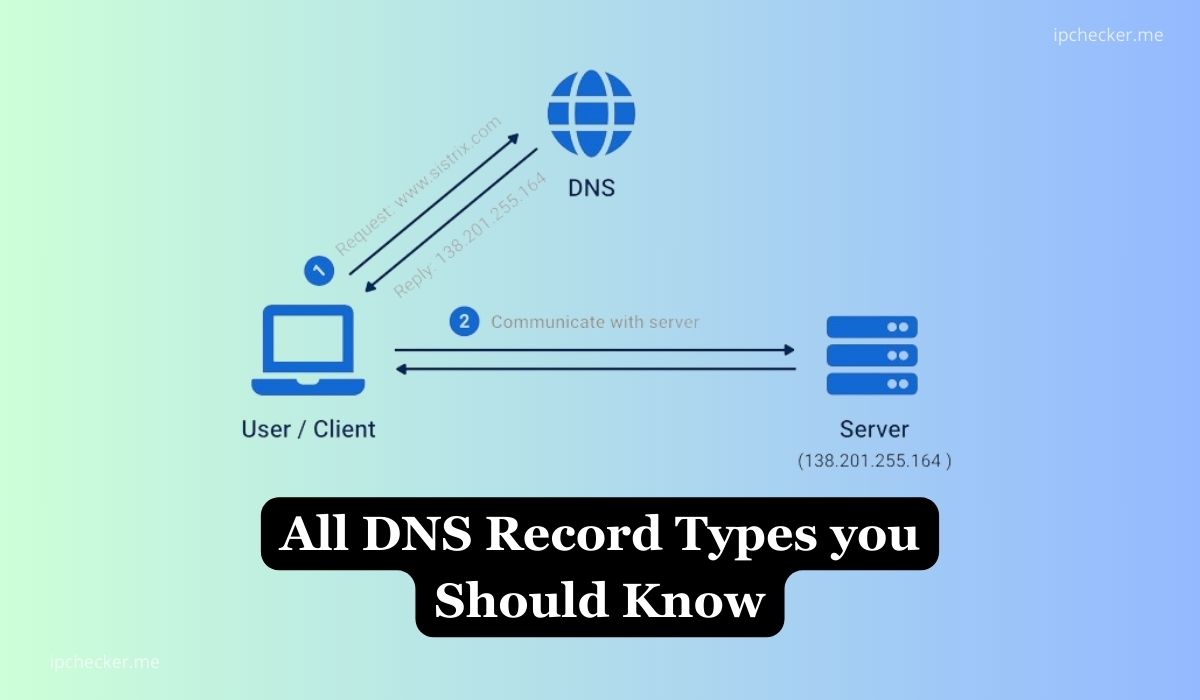
DNS record types refers to DNS uses various record types to store different kinds of information associated with domain names.
What is DNS?
DNS (Domain Name System) is a hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network.
Related: What is Global DNS Propagation
Suggested: What is a Virtual IP Address – Purpose and Benefits
What Are DNS Records?
DNS records are essentially entries in a database that map human-readable domain names to IP addresses or other information. They serve as the backbone of the internet, translating domain names into numerical IP addresses that computers can understand to locate services or resources on the internet.
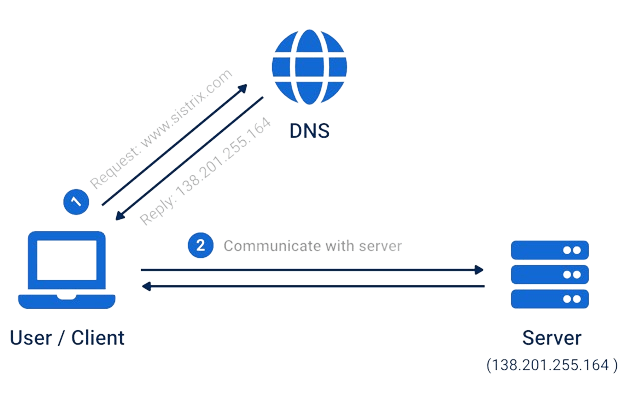
8 Most Common DNS record types
There are various dns record but below are the common DNS record types:
- A (Address) Record: This record maps a domain name to an IPv4 address. For example, example.com might be mapped to 192.0.2.1.
- AAAA (IPv6 Address) Record: Similar to A records but for IPv6 addresses. It maps a domain name to an IPv6 address.
- CNAME (Canonical Name) Record: This record creates an alias for a domain name. It is often used when a domain needs to point to another domain, such as when www.example.com points to example.com.
- MX (Mail Exchange) Record: This record specifies the mail servers responsible for receiving email on behalf of the domain. It points to the domain’s mail servers. For example, mail.example.com might be listed as the mail exchange server for example.com.
- TXT (Text) Record: This record can contain any text data, but it’s commonly used for various purposes such as domain ownership verification, SPF (Sender Policy Framework) records for email authentication, and more.
- NS (Name Server) Record: This record specifies the authoritative name servers for the domain. It indicates which servers are responsible for hosting the DNS records for a domain.
- PTR (Pointer) Record: This record is used in reverse DNS lookups to map an IP address to a domain name. It’s the opposite of an A or AAAA record.
- SOA (Start of Authority) Record: This record indicates the authoritative server for a DNS zone and contains administrative information about the zone, such as the primary name server, the email of the domain administrator, the serial number of the zone, and various timers relating to refreshing the zone.
Related: IP Address and How to Use IP Checker
All DNS Record Types you Should Know
These are all the DNS record types that are currently in use:
- A — IPv4 address
- AAAA — IPv6 address
- APL — Address prefix list
- AXFR — Authoritative zone transfer
- CDNSKEY — Child copy of a DNSKEY
- DNAME — Delegation name
- KEY — Cryptographic key for DNSSEC (obsoleted by DNSKEY)
- KX — Key exchange
- AFSDB — AFS database location
- DNSKEY — Cryptographic key for DNSSEC
- DS — Delegation signer
- CAA — Certification authority authorization
- HINFO — Host information
- HIP — Host identification protocol
- CDS — Child copy of DS
- CERT — Cryptographic certificate
- CNAME — Canonical name
- EUI48 — MAC address (EUI-48)
- EUI64 — Mac address (EUI-64)
- CSYNC — Child-to-parent synchronization
- DHCID — DHCP identifier
- DLV — DNSSEC lookaside validation
- HTTPS — HTTPS binding
- IPSECKEY — Cryptographic key for IPsec
- SIG — Resource record signature for DNSSEC (obsoleted by RRSIG)
- TKEY — Transaction key
- IXFR — Incremental zone transfer
- LOC — Geographical location
- MX — Mail exchange
- NAPTR — Naming authority pointer
- NS — Name server
- TXT — Human-readable text
- URI — Uniform resource identifier
- ZONEMD — Message digest for DNS zones
- NSEC3 — Next secure (version 3)
- NSEC3PARAM — Parameter for NSEC3
- NSEC — Next secure (obsoleted by NSEC3)
- NXT — DNSSEC key (obsoleted by NSEC)
- OPENPGPKEY — Public key for OpenPGP
- OPT — EDNS option
- PTR — Canonical name pointer
- RP — Responsible person
- RRSIG — Resource record signature for DNSSEC
- SMIMEA — S/MIME association
- SOA — Start of authority
- SSHFP — Public key fingerprint for SSH
- SVCB — Service binding
- SRV — Service locator
- TA — Trust authority for DNSSEC
- TLSA — Certificate association for TLS
- TSIG — Transaction signature
Also read: What is VPN?
Also read: What is my IP Address? – IP FAQ
Useful Domain Tools
Useful Web & SEO Tools
– Webtools