What is a Virtual IP Address?
A Virtual IP Address (VIP) is an IP address that is not bound to a specific physical device or network interface. Instead, it is associated with a cluster or group of devices, servers, or instances. The primary objective of a VIP is to provide a single, consistent IP address that represents multiple underlying resources. This abstraction allows for seamless communication and interaction with the cluster, even if the individual devices within the cluster may change due to factors such as load balancing, high availability configurations, or failover mechanisms.
Also read: What is VPN?
What is the Purpose of a Virtual IP Address?
The purpose of a VIPis multifaceted and serves several key functions:
1. Load Balancing: Virtual IP Addresses are often used in load balancing scenarios, where incoming traffic is distributed across multiple servers or nodes to optimize performance and prevent overload.
2. High Availability and Failover: VIPs contribute to high availability setups by facilitating failover mechanisms. If one server or node fails, the VIP can quickly and transparently redirect traffic to a healthy resource, ensuring uninterrupted service.
3. Simplified Network Management: VIPs simplify network management by abstracting the complexity of routing and addressing, allowing administrators to focus on overall system architecture.
4. Scaling: In dynamically scaling environments, VIPs enable easy addition or removal of resources without requiring changes to external systems.
Also read: What is my IP Address? – IP FAQ
How Does a Virtual IP Address Works?
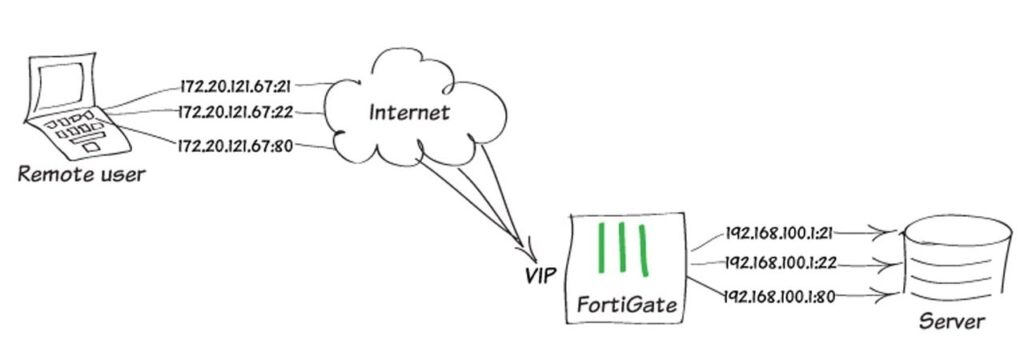
A VIP Address operates by using network protocols and configurations to create a layer of abstraction over physical resources. The process involves:
1. Configuration: The network administrator configures the VIP and associates it with the cluster or group of devices.
2. Network Communication: Incoming traffic is directed to the VIP, which acts as a central entry point.
3. VIP Routing: The network infrastructure routes traffic to the appropriate destination within the cluster based on predefined rules, load balancing algorithms, or failover mechanisms.
4. Resource Interaction: The VIP directs traffic to available resources, which may change dynamically based on various factors.
Also read: 6 Effective Methods to Track IP Address
Benefits of a Virtual IP Address
Below are benefits of VIP Address:
1. VIPs contribute to high availability by ensuring seamless failover in the event of hardware or software failures, minimizing downtime.
2. VIPs enable efficient distribution of incoming traffic across multiple resources, optimizing resource utilization and performance.
3. Administrators can perform maintenance tasks on individual resources without disrupting overall service, as the VIP redirects traffic to healthy resources.
4. VIPs support easy scaling by enabling the addition or removal of resources without affecting external systems.
Also read: What is global DNS propagation
Difference Between a Static IP Address and a Virtual IP Address
Static IP Address:
A static IP address is assigned to a specific physical device and remains constant over time. It is suitable for situations where a device requires a consistent, predictable address for remote access or network services.
Virtual IP Address:
A VIP is not tied to a single device but represents a group of resources. It is often used for load balancing, high availability, and failover scenarios.
Virtual IP Address vs. Floating IP Address
While similar in concept, VIP and floating IP addresses have subtle differences:
1. Virtual IP Address: A VIP is an IP address assigned to a cluster of devices to facilitate load balancing and failover.
2. Floating IP Address: A floating IP address is typically associated with a virtual machine (VM) in a cloud environment. It allows the VM to quickly switch between different physical hosts while retaining the same IP address.
Also read: Difference between IPv4 and IPv6
How to Get a Virtual IP Address
You can obtain a VIP by configuring network settings and load balancers. Simply follow the steps below:
1. Choose a load balancer solution that supports VIP addresses and meets your requirements.
2. Set up the load balancer to distribute incoming traffic among the resources in the cluster.
3. Configure the virtual IP address and associate it with the cluster or group of resources.
4. Define failover rules to ensure seamless redirection of traffic in case of resource failures.
5. Thoroughly test the VIP configuration and continuously monitor its performance and functionality.
Also read: IP Address and How to Use IP-Checker
